10. Remote connection by Internet, Security and access
10.1 Introduction - 1. The risks (virus, hacking, ...) - 2. Basic connection Internet - 3. Various points of a professional connection - 4. Hardware and software firewall - 5. The remote access
This chapter deals with communication and security between computers. The most common concerns the connection to INTERNET (Firewall, VPN) but also of takeover of PC or network remotely from a computer connected to a phone line or via the INTERNET (data sharing), work remotely... All these connections can be processed in hardware or software, are two possibilities exist systematically. We will see in detail the hardware possibilities. This will prepare following course: architecture of a network.
1. Risks
A brief on the security risks (viruses, hacking,...). An explanation more complete on viruses, adware, spyware,... is included in the INTERNET safety course. Anti-virus Hardware level, some routers and VPN include an internal anti-virus. Other devices are specialized: PANDA produces a model of this type. The benefit comes from the automatic daily updates on a single node: router input / output of the Internet connection to the internal network. When a virus is detected in an email (any type), the mail is directly returned to the sender without even going on the internal network or the PC of the recipient. The default remains the other entry points: floppies, pirated CDs, Internet connections via other points (modem laptop for example). Spyware, adware, dealer,... using port 80 (navigation), they are not detected by the hardware firewall, but by the anti-virus hardware.
1.1 Hacking, security of the PC
Various methods of hacking will be examined.
 The first method involves injecting a program in your PC (via email, for example). This server will respond to any request from a client (the program that tries the intrusion) via a TCP or UDP port. The ports are specific to each trojan (also called
backdoor). As these programs are easily downloadable on the Internet, any kid is capable of using. On the other hand, it requires that a program be implemented in your computer or PC from the network: If the client software is not implanted in the system, no
risk.
The first method involves injecting a program in your PC (via email, for example). This server will respond to any request from a client (the program that tries the intrusion) via a TCP or UDP port. The ports are specific to each trojan (also called
backdoor). As these programs are easily downloadable on the Internet, any kid is capable of using. On the other hand, it requires that a program be implemented in your computer or PC from the network: If the client software is not implanted in the system, no
risk.
The second method uses security vulnerabilities in the Microsoft stuff, be it in the Windows operating system, Internet Explorer, Outlook or Office (all versions combined). This solution is more reserved to professionals. This allowed a firewall test site to open my CD-ROM drive remotely. With a firewall software on the station and the network protected by a hardware firewall, I smelled but rather safely. The solution is to follow the SERVICE PACK of Microsoft security.
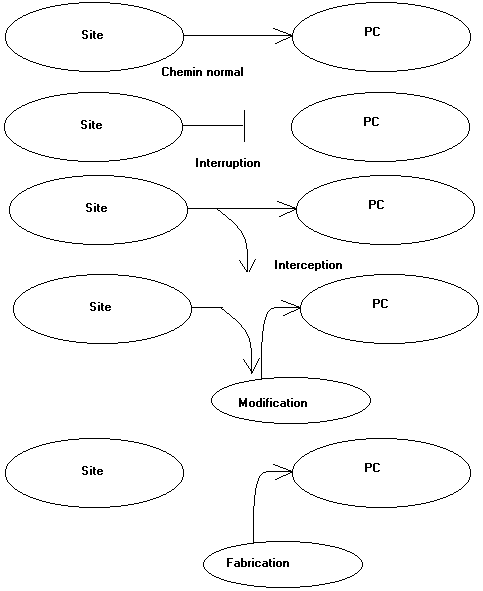
Third, by far the more insidious, the method is to modify information in the frame TCP/IP to a correct message to the PC (or router) attacked believes that the information from indeed site request as in the diagrams below. This technique is called spoofing. To counter these attacks, it is imperative that frames is all analyzed before reading by the browser.
The goals are multiple: flights information and in many cases, used this computer as a relay for other attacks. The target then detects the attack as from the "hacked" PC .
1.2. Attacks by Denial of Service.
This type of attack is to send a maximum of query on a web server or a router in a minimum of time. The device knowing more follow crack literally.
The method is to send multitudes of ICMP echo-requets packets by modifying the source address of each packet. The commands sent are multiple packets of 64 Kb or less (remember the PING command parameters). The target can no longer meet the demands of connections because all of the bandwidth is limited.
This is the method of the spoiled kid who is unable to fit into a server, then, it crashes. On the other hand, it is also a much more professional to stop Internet servers with a maximum of commands at the same time, the best is to use a maximum of computers for the attack using those infected with a trojan.
1.3 Station Deny of service(tear drop, new tear, boink...)
The attacks of the type Teardrop, Newtear, Boink... are almost identical to the refusal of service above except which it tackles only with the computers (servers included) directly connected or even via a router. This type of attack aims at the system Windows 32 bits (Win 95, 98, Me, XP (Pro), NT and 2000) but also the operating systems Linux lower than 2.0.32 (as Linux is not in my competences, to check). Apparently, Mac and Unix systems can also be deteriorated by these attacks. With share Windows 3.11 and DOS (but how to navigate on Internet with DOS?), all are thus aimed. The attack is not done any more on one server, but on the connected stations. This type of attack consists in sending packets TCP/IP which overlap called OOB = Out Of Band). The target computer tries to rebuild information and finally, not arriving there, this causes a planting of the machine. In Windows, you find yourselves with a beautiful blue window and you have other choices only to start again the machine.
1.4. Some complementary details.
Anonymity on Internet, not so sure. To determine your address IP provided by the provider is easy for website (a single command in PHP language). A router protects your local address TCP/IP on the network by not indicating that the external address. In the case of a division of connection via the programs provided with the operating systems Microsoft, in fact the internal addresses of the network are directly detected. Any intrusion, attacks of any type initially requires of the "hacker" to know address TCP/IP of the target with respect to Internet. The sport for him is then to know the internal addresses of stations PC or others of the network. As long as the address Wan (Internet) is invisible, it cannot anything. Inevitably, it is easier A to detect when the local area network is connected by fixed address TCP/IP.
In the same way, your operating system and your navigator Internet are automatically sent by your navigator to the site, idem for the resolution of your screen (dimension and a number of colors)
The servers proxy are memories hiding place which make it possible to accelerate connections. The mechanism is simple, when a page has been just read, the proxy the guard in memory. If a request on this page intervenes quickly, the proxy does not download it Internet but directly of its memory. Moreover, it is more difficult to track you since you are not always directly in contact with the sites. These proxy can be external cases, included in a dedicated computer of the local area network (under Linux for example) or directly by the provider.
Cookies are small textual files charged on your computer. These cookies records your preferences. This makes it possible for example to arrive directly on the French version of Google.be. Not quite dangerous, but these cookies often includes information such as passwords (even if they are often encrypted) or goes back it to your last visit on a site. Some cookies makes it possible to track you on various sites.
NAT (Network Address Translation) is used as translation between the outside of the local area network (Internet) and the stations. The router builds a table of correspondence of IP addresses. In this manner, outside cannot determine the internal address of a station. With the reception of data by the router, this one transfers information towards the true recipient thanks to his table.
2. Basic connections Internet.
INTERNET connection sharing allows to connect several computers networked TCP/IP simultaneously with a single modem. Professional sharing is done via a router, but simpler shares directly use a modem connected to a PC. The modem can be normal, ISDN or ADSL. Similarly, the type of modem can be internal, external serial, external USB or even in certain ADSL modem, which is connected via a network adapter. In the first three cases, sharing can be done directly by the operating system (from Windows 98 Second edition). In the case of a link via network adapter, sharing can be done via a router via a software type WinGates. This solution is directly located in the 2003 and 2008 servers. These programs also provide the security of connections. In the latter case, the PC providing sharing receives 2 network cards.
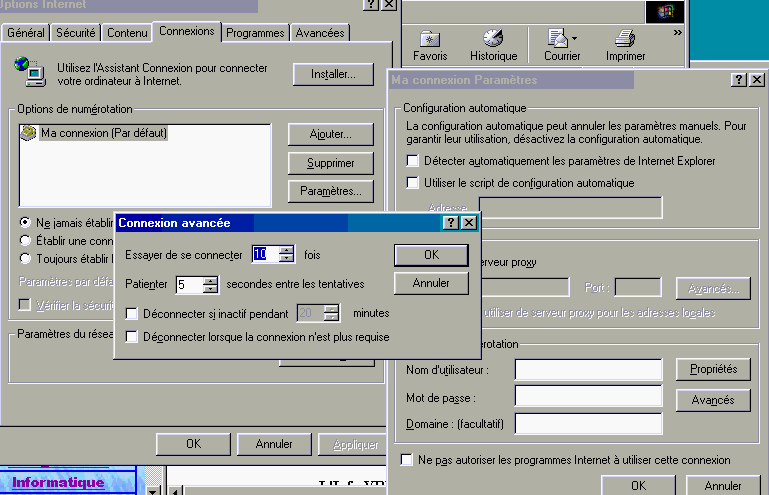
In the case of a simple sharing via Windows, each computer can request the Internet connection, but it can be cut on the PC connected to the Internet. This poses no problem in ADSL, but attention to PSTN or ISDN (ISDN) telephone communications. You can cut the INTERNET connection after a certain period of inactivity by the Internet Options command in. Select the connection (my connection below) and click on the settings button. In the next window, select the 'Advanced' button. Check the disconnect if idle for and type the number of minutes desired.
Different software or hardware solutions will be connected between the network and Internet, either to ensure the safety, or to ensure the speed of connection. These equipments (software) provide various functions of connection.
3. Various points of a connection/professional division Internet.
3.1. Basic sharing
Before talking about the devices and solutions to implement for professional Internet connections, analyze the different possible problems. This will allow futures to draw our connection easier.
In the case of a connection to the INTERNET, the first task is the sharing. This will allow multiple users to connect to Internet at the same time (navigation, mail, news,...). This necessarily involves a network installation. In this case, a computer or a device (usually a simple PC on which the modem is connected should be binding.
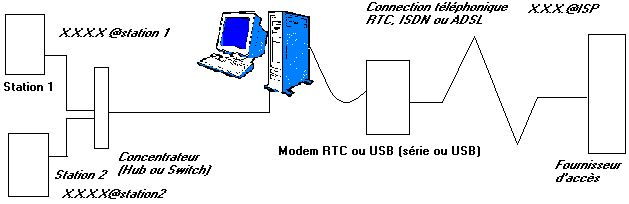
According to diagrams' above, each station has its own address TCP/IP (X.X.X.X.@station1 and X.X.X.X@station2). In the same way, the supplier of access automatically provides an address TCP/IP to connection. At the time of a request for posting of a site, referred by a clean address TCP/IP, for example 238.128.128.128 which we will name by X.X.X.X@site. At the time of the request for posting, station 1 sends to the apparatus of connection its own address (for the answer) and site addresses it which she wants to post (X.X.X.X@site). The supplier of access and all the components of Internet network will manage so that information of the site is returned to address TCP/IP Internet provided by the supplier of access (X.X.X.X.@ISP) which returns them to the apparatus of connection. This one will make the transfer of its own address Internet towards the private address of station 1.
Operation, though complex in an internal way, is not too difficult to implement with the current software. This method is used by the division of connection Internet established in Windows 98 SE and later. This solution is not very protected. Each address of the connected PC is visible of Internet. This practice is used for small divisions of family connections Internet out of modem STN or ADSL with modem USB.
3.2. Sharing using a specialized software.
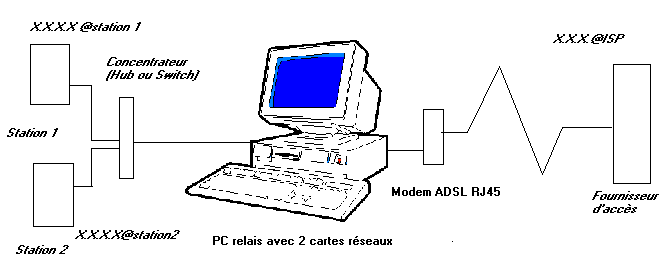
This solution of division Internet uses a PC relay between the network and Internet. The PC uses 2 networks cart. A NIC is connected towards the internal network, the second network card is connected to a modem Ethernet RJ45. The software can be Wingate, some professional solutions (Symantec for example) or a solution containing Linux. This diagram is used by Windows 2003 and 2008 server. The PC relay must remain connected so that connection Internet functions.
The software provides various functions: NAT (Network Address Translation), proxy (mask) and even firewall. The firewall if it is directly established (Linux) is of functionality identical to a firewall hardware. You can also install on this PC relay a firewall software. This software solution is part of the other courses of second year, in particular Linux.
3.3. Sharing via a simple router.
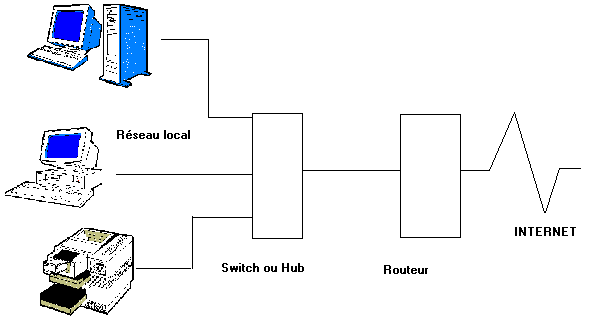
The use of Internet is completely transparent for the network. The router remains connected permanently. This hides the internal network (addresses PC and peripherals) for outside, but does not prevent the risks of intrusion. Indeed, separately the hidden addresses (NAT), the stations are directly connected on Internet. A Trojan on a station will communicate through the network in a completely transparent way. It is even probable that the hacker will not realize that it is in a network that at the time of the takeover of the PC when it has access to all the divisions of files and peripherals.
3.4. Sharing via router and firewall hardware.
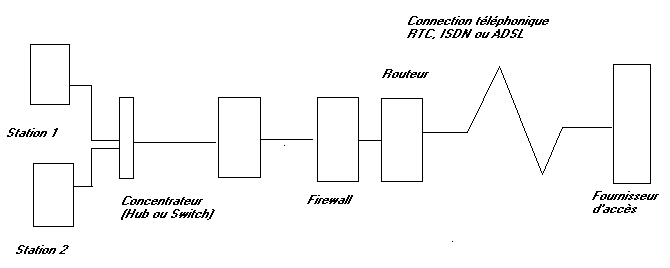
This diagram represents almost the solution of ideal safety (almost worries me). The router and the firewall can be included in the same case. The modem can be integrated in the router or be connected between this one and Internet. This solution will be examined in a exercise of chapter 17. Sharing and connection Internet via a router - firewall mode ADSL RJ45 Ethernet.
Safety does not rest on the assembly but on the manner of parameterize the firewall. This is valid for all the solutions of safety firewall.
3.5. The DMZ (Demilitarized Zone).
This is a particular use of the firewall. It is used with a lodging on a server specific to the company or in the event of lure for various attacks. In this last case one by the PC bastion. Its use as server proxy or server of transport is also used.
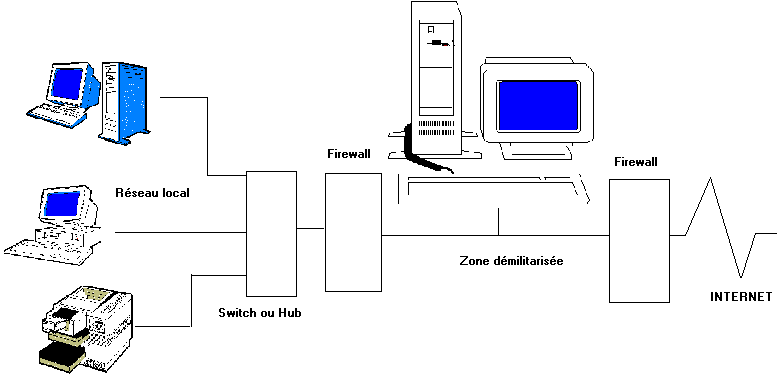
The firewall in contact with Internet will let pass information on port TCP 80 (possibly 443) coming from the outside of the site, as well as information coming from the internal site towards Internet. In the case of a Web server, the first firewall avoids the attacks outside. Ports 20 and 21 for example could be closed. On the other hand, information coming from outside will pass is by the external firewall, then by server DMZ (case of a PC bastion) then by the second firewall.
It is not the maximum level of safety, but the hacker is found with 2 to see 3 barriers to be opened.
4. Firewall
The firewall protect the processing installations from hacking. It supervises the communications of computers towards Internet and screw poured. For that, it analyzes, blocks or authorizes the communications via ports UDP and TCP. This is valid for connections Internet, but also between various parts of an internal network. A broad part of the "intrusions" are orchestrated interior of the company. Think for example of the employee who has just received his notice... One finds 2 types of firewall: software firewall and the firewall hardware.
The parameter setting of the software firewall does not form part of this course hardware, I will not be delayed there.
In applications Internet, to facilitate the communications between identical applications, one uses ports as well in TCP as in UDP. Each port is specific to a type of application. Navigation is done by port 80 and the news by port 119 for example. The parameter setting consists in opening doors (ports) necessary to the normal applications according to the emission or TO addresses IP (at exit) (addresses of the sites). As of this moment, it seems to to me clear that all the others must be closed. By definition, the intrusion is always done by the weakest entry of the protection of the network. This is similar with the safety of a building. That is not used for nothing to put doors armored everywhere, if the window of behind remainder opened permanently.
4.1. Difference between a software and hardware firewall
Both do not make exactly the same job: they are complementary.
A software firewall checks and indicates on which ports the programs that access the Internet from your PC (TCP/IP and UDP). Similarly, they announce the ports on which returning (or attempt to return) applications on your PC. In this sense, except poor configuration, they are effective. On the other hand, they analyze all the routines (changes to the frames,...), nor analyze still less the security flaw of the OS (different security vulnerabilities Microsoft on operating systems, Internet Explorer, Outlook, and same office). By checking the programs attempting Internet connections, these programs block spyware and adware. Unfortunately, this solution generally also blocks the INTERNET connection. A software firewall is installed on each PC (where a heavy admin work), on the server or on a dedicated PC. In addition, such software rarely recognize the external (Internet) addresses of internal addresses. These programs are perfect for backdoor detection. If they detect them, they do not suppress them. This role is given to anti-virus, even if the anti-virus do not consider adware and spyware as harmful (these are commercial programs).
A firewall hardware is placed between the INTERNET and the network. In this sense, the intrusions (or attempts) within the network are never analyzed. Even if a hardware firewall is not associated with Microsoft, they not protect security of programs and operating system. By analyzing data frames, they reject also the intrusions by addresses modifications. On the other hand, even if all of the unused ports are closed, programs that use the standard ports can work without problems. A verse (trojan) that would use port 80 will be blocked any, it is considered as a standard application. Spyware and adware using port 80 are therefore under no circumstances taken into account by a hardware firewall.
Two protections below are generally integrated in the firewall material:
Statefull Packet
Inspection:
Allows the firewall to compare a package of data entering with the packages
having previously been regarded as "healthy".
Content Filtering :
In particular allows to control the accesses to the Web by filters (based on
lists of Internet addresses, words key or time beaches of connection).
An optimal safety would be a firewall hardware between the network and Internet and a software firewall on each station. Nevertheless, the internal firewall in the case of heavy networks poses problems on the level user. With the slightest warning (even useless of type DHCP on port UDP 68), the administrator will be called (or not...) by the user.
Currently various firms manufacture networks cards which include a firewall hardware (Nvidia).
4.2. Ports to be opened in TCP and UDP, the beaches of addresses.
Each application is characterized by a port TCP and/or UDP used. It is specific to the type of application This facilitates the communications since an application of the navigation type will use office port 80, whether it is Microsoft Explorer, Netscape or another. The numbers of ports (as well in TCP as in UDP) vary from 0 to 65535 (216). IP determines the address of the site or the PC in communication. The combination port TCP/IP thus determines the site and the application.
4.3. Method of detection of a firewall hardware and functionalities
The firewall analyze the trames, while the firewall software analyze the applications. This analysis hardware is carried out by an internal software. The first part filters combinations TCP IP to send or not information towards the PC customer of the network. The second part will check if information is actually required by a station customer by analyzing connections PC - Internet site.
The third application is called State full inspection. This term is patented by Checkpoint (one of the leaders of safety Internet) which manufactures firewall software but whose technology is established in various firewall hardware, in particular those manufactured by firm NOKIA. "State Full Inspection" is also called Firewall-1 or with technology of dynamic filtering. The firewall determines if the customer is well connected (activates) on Internet at the time of the reception of the message. For that, the firewall guard in tables of connection active sessions. In the contrary case, the message is purely blocked.
The firewall can include also various options such as the proxy. A proxy is a hard disk space on which the usually required pages are stored. Each provider uses a proxy for connections. At the time of a request, the proxy checks if the page is not in memory. In the positive case, the page is returned to the request without remote loading starting from the site. This makes it possible to save time at the time of the remote loadings. This solution is also used in some firewall or router. If the user is not in direct contact with the site, its address IP could not be analyzed. Though certain sites say some, it is not really a safety since the addresses with hacker are often determined by a addresses scanning on Internet. On the other hand, in the case of the firewall which do not return orders PING, this allows the attacker to determine that the address is actually used if the proxy is not in function. Notice that use ICQ or MSN Messenger also makes it possible to determine your address TCP/IP even more easily, the list appears on the site.
The filtering of sites is established in the majority of the firewall hardware. This makes it possible to block the outgoing accesses of the addresses of sites or even of the addresses containing a word. You can for example block the sites whose name included sex, meets or KAZAA.
5. The remote access to a network
This application makes it possible to be connected to an internal network via a telephone link or by Internet.
5.1. Takeover remote and file transfers.
In the preceding chapter, we saw that the horse of the Netburst type make it possible to take the remote control (amongst other things) of a PC via Internet. This solution seems easy but makes it possible others to take control too. This solution is thus completely to proscribe.
The solution most commonly used calls upon software of the type PC Anywhere which makes it possible to take the ordering of PC via analogical modems or ISDN, or even ADSL (Internet). This solution is often used for small infrastructures of the independent type, or for the breakdown service of the remote users in the internal networks. Many attempts at attacks by Internet come from this software. The parameter setting of PC Anywhere makes it possible to change the number of port for the remote access. It is not the perfect solution. Indeed, for a remote takeover, one needs the number of port and the program customer. By changing the number of port, the administrator supposes that the hacker will not be able to take control. Other side, the hachers by scanning of addresses on all the ports, receives the software which answers (even badly) on a port. It does not have any more but to test all the possible programs on this port. The takeover is also done by password (clearly advised).
Another solutions which is not used that by certain programs allow to share resources via the access remote network.
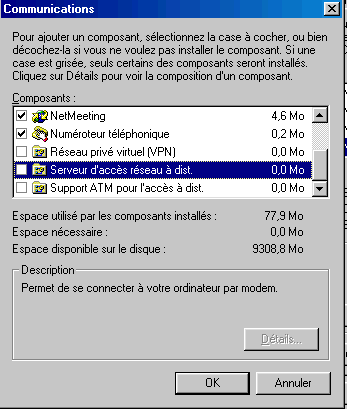
This function requires the installation of an additional component of Windows: server of access remote network and allows the use of files on discs divided via a modem (always RTC or ISDN). Connection to allow the entry is also done via a password and the starting of this server of remote access via the part access remote network.
Certain office automation programs (in particular Works of Microsoft) also include transfer transfer functions of files. Windows XP also established a function of remote order taking, by hoping that here also there are no faults of safety.
5.2. Virtual Private Networks (VPN)
The solutions above directly do not make it possible "to be connected to a server network", but to take the control of a PC which him is connected to the network. They are software solutions.
VPN (for Virtual Private Networks) equipment are connected physically on Internet or between the network and the router following the models. The last versions of the operating systems servers of Microsoft establish equivalent functionalities.
VPN create between a computer and the network interns a protected and encrypted connection to ensure the transfer of information: called a tunnel commonly. When the station requires via Internet a connection on the internal network, the 2 apparatuses communicate a software key which will be used for encoding of information. The VPN creates a kind of tunnel made safe on Internet which prevents any form of hacking. This solution is the only usable one for a connection via ADSL connection requires 3 things:
- A particular software on the customer (virtual private Network installed like component of Windows or specific program)
- A material hardware of the type VPN connected between Internet and the corporate network (possibly Windows 2000 or XP)
- An address Internet TCP/IP fixed or at least known at the time of connection.
The first two constraints seem easy. We will speak again of the apparatus. The third requires, that is to say an Internet site and thus a clean server connected on Internet, even if connection must be done on another server or a specific subscription making it possible to have a fixed address Internet TCP/IP. In the case of a normal subscription ADSL, the address changes with each connection and the maximum after a few tens of hours following the provider. The amateurs will be able nevertheless to use some solutions to know address TCP/IP of connection to one moment given on specific sites for example and to communicate it via telephone or mall. This solution is not very possible for a connection 24h/24h.
One distinguishes several models from VPN. The majority of the models hardware allow only one tunnel between 2 network installation fixed. They thus do not allow the domestic industry (though publicities imply). The models more expensive also allow remote work. The mode of encoding can be MPLS or IP-Dryness (IP Security). Encoding is done only between the two VPN. Certain methods of tunnel, in particular Over IP (with the difference of tunnel IP) make it possible to make forward other protocols such as IPX in the tunnel.
In the case of the use of a VPN, you cannot make safe your network by preventing the division of the resources via TCP/IP. Indeed, for small networks, you can establish in parallel with TCP/IP the protocols IPX or Netbui and configure protocol TCP/IP network on the network card so that it does not allow the division of the resources. The VPN makes it possible to use at distances all the resources of the network (files, applications and peripherals of the printer type) as if you were directly connected on the network.
According to the apparatus (of the software solutions exist, in particular in Win2000 server), the VPN will carry out several tasks like below the series of Symantec Gateway security.
A footbridge (gateway) towards Internet (function of router Internet), a function of firewall to block the intrusions, an integrated antivirus and function VPN to create tunnel Internet via, generally operation is in conformity with the specifications of IPsec encoding of the stations customer.
 The VPN will provide a local address to a PC
connected on Internet this one then automatically will be integrated in the
network. Attention, the parameter setting of this type of apparatus on level VPN
is generally more pointed since it makes it possible for example to accept the
data returning on an address but to refuse the outgoing entries.
The VPN will provide a local address to a PC
connected on Internet this one then automatically will be integrated in the
network. Attention, the parameter setting of this type of apparatus on level VPN
is generally more pointed since it makes it possible for example to accept the
data returning on an address but to refuse the outgoing entries.
When all the levels are solved, you can directly connect two internal networks VIA Internet. It is currently the only viable solution (without completely dedicated and rented lines) for this kind of applications. It is also, at least in Belgium in the zones connected to the ADSL, the best solution for the telecommuting (work starting from its residence).
In relation:
- Modem: Course: modem RTC, ISDN
- ADSL splitter How to install filter ADSL on the telephone line
|
Next of Hardware 2 training > Chapter 11: Wireless network |
The Hardware 2 course: Network, server and communication. - The complete hardware training
© YBET 2006 - 2015
